AC vs. DC EV Charging: What’s the Difference and Which One Do You Need?
Sep 12,2025
I struggled to pick the right EV charger. AC and DC terms confused me. Let me explain them simply.
AC charging is slow and cheap, great for the home. DC is fast and costly, perfect for quick road stops.

EV Charger Setup
EV charging can feel tricky. I’ll cover the basics, compare options, and show how Parwatt makes it easy for your business.
- The Basics: How Does an EV Battery Actually Charge?
- AC Charging (Alternating Current): The Everyday “Top-Up”
- DC Charging (Direct Current): The “Quick Boost” for the Road
- Side-by-Side Comparison: Speed, Cost, and Use Cases
- So, Which One is Right for You? A Simple Guide
- The Future: How Parwatt Simplifies Both AC and DC Charging Solutions
- Conclusion
The Basics: How Does an EV Battery Actually Charge?
My first EV confused me about charging. Let’s make it simple.
EV batteries store DC power. AC charging converts power in the car. DC chargers convert it outside, making it faster.
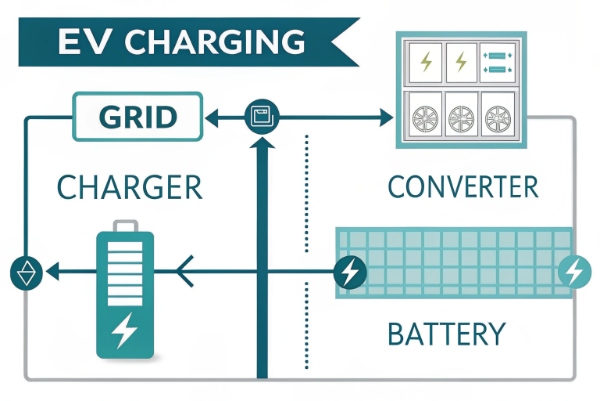
EV Battery Charging Process
Why It Matters for Your Business
EV batteries need DC power. AC charging uses the car’s charger to turn AC into DC. This is slow. DC charging converts power outside the car. It delivers DC to the battery. This is fast but needs bigger equipment. For charge point operators or fleet managers, this helps you choose chargers. Here’s a quick look:
| Aspect | AC Charging | DC Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion | Inside car (slower) | Outside car (faster) |
| Speed | 3-10 hours | 16-50 minutes |
| Equipment | Smaller, simpler | Larger, complex |
This helps you plan charging setups. It meets needs for employees, tenants, or drivers on the road.
AC Charging (Alternating Current): The Everyday “Top-Up”
I charge my EV at home each night. Slow charging works for me. AC might work for you too.
AC charging is slow but cheap. It’s great for home or work, perfect for overnight or long parking.

AC Charger at Home
Why AC Fits Your Routine
AC charging uses standard outlets. It’s easy to find and costs less. For real estate or workplace clients, AC chargers are simple to install. They fit in parking lots or garages. The slow speed (3.6 kW to 7 kW+) is good for overnight charging. This saves money compared to DC. It’s better for battery health. My home charger was cheap to set up and works well daily. Here’s a quick look:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Speed | 3-10 hours (3.6 kW to 7 kW+) |
| Cost | About half the cost of DC per kWh |
| Best Use | Home, work, long-term parking |
For retail chains or municipalities, AC chargers meet tenant or employee needs without high costs.
Learn more about Parwatt’s AC wallbox chargers
designed for workplaces and residential projects.
DC Charging (Direct Current): The “Quick Boost” for the Road
I needed a fast charge on a road trip once. DC charging helped me. It’s great for quick stops.
DC charging is fast and costly. It’s perfect for public stations or highways for quick battery boosts.

DC Fast Charger
Why DC Suits Public Needs
DC chargers turn AC into DC outside the car. This sends power straight to the battery. Speeds range from 50 kW (~50 minutes) to 150+ kW (~16 minutes). For charge point operators or energy utilities, DC chargers attract drivers needing fast charging. They’re bigger and cost more to install, but they handle high demand. Battery preconditioning improves charging speed. I’ve seen drivers save time with this. Here’s a breakdown:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Speed | 16-50 minutes (50 kW to 150+ kW) |
| Cost | Higher per kWh than AC |
| Best Use | Public stations, highways |
DC chargers work well for fleet operators or hospitality chains serving customers on the move.
Explore Parwatt’s DC fast charging solutions here
Side-by-Side Comparison: Speed, Cost, and Use Cases
Picking between AC and DC was hard for me. Let’s compare them to help you decide.
AC is slow and cheap, great for daily use. DC is fast and costly, perfect for public charging.
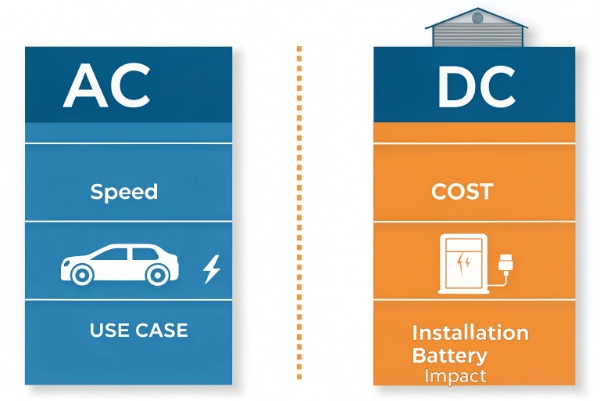
AC vs. DC Comparison
Breaking Down the Differences
AC and DC fit different needs. AC chargers are small and cheap. They’re good for routine charging at home or work. DC chargers are powerful but expensive. They’re made for speed at public stations. For automotive OEMs or resellers, offering both covers all customers. Here’s a detailed look:
| Criteria | AC Charging | DC Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 3-10 hours (3.6-7 kW+) | 16-50 minutes (50-150+ kW) |
| Cost per kWh | About 50% cheaper than DC | Higher due to equipment |
| Use Case | Home, work, overnight | Highways, public, quick stops |
| Installation | Cheaper, smaller space | Costly, larger space |
| Battery Impact | Better for battery life | Good for short cycles |
This helps businesses like CPOs or fleet operators balance cost and performance for customers.
So, Which One is Right for You? A Simple Guide
I wasn’t sure which charger I needed. Let’s find the best fit for your business.
Use AC for daily, cheap charging. Choose DC for fast, public charging. Combine both for flexibility.

Charging Decision Guide
Matching Chargers to Your Goals
Your choice depends on your customers. For workplace clients or real estate developers, AC chargers are cheap and practical. They support employee or tenant charging. For CPOs or hospitality chains, DC chargers attract drivers needing quick stops. I suggest using both: AC for daily use, DC for urgent needs. This balances cost and convenience. Battery health matters too—AC is gentler, DC suits quick bursts. Here’s a guide:
| Business Type | Best Charger | Why |
|---|---|---|
| CPOs, Fleet Operators | DC (50-150+ kW) | Fast charging for public, fleets |
| Real Estate, Workplace | AC (3.6-7 kW+) | Cheap, long-term charging |
| Mixed Needs | Both AC and DC | Covers all use cases |
This plan ensures efficiency and happy customers across industries.
The Future: How Parwatt Simplifies Both AC and DC Charging Solutions
I’ve watched EV charging grow. Parwatt leads with smart, scalable solutions.
Parwatt offers AC and DC chargers with AI, supporting ultra-fast and wireless charging for businesses.

Charging Solution
How Parwatt Meets Your Needs
EV charging’s future is exciting. Ultra-fast DC chargers (150+ kW) are growing. Wireless charging removes cables. Parwatt’s solutions use AI for smart energy management. This helps utilities or municipalities balance grid load. Our chargers support OCPP for CPOs, offering real-time monitoring. For OEMs, we provide custom ODM modules. Our small AC chargers fit real estate projects, while strong DC chargers serve fleets. Here’s what we offer:
| Solution | Benefit | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Smart AC Chargers | Cheap, easy to install | Real Estate, Workplace |
| Ultra-Fast DC | Fast charging, high demand | CPOs, Hospitality |
| AI Integration | Saves energy, cuts downtime | Utilities, Municipalities |
Parwatt’s technology ensures scalability and reliability, helping businesses lead in the EV market.
Conclusion
AC is cheap for daily use; DC is fast for public needs. Parwatt makes both simple with scalable solutions.
--- END ---
Already the last article
Next: Electric Vehicle Charging: Everything You Need to Know?
Related Posts
Industry News
Industry News
Product News





